See geocaching, geotagging and geodetic coordinates. (2) ( Geostationary Earth Orbit) A communications satellite in orbit 22,282 miles above the equator. At this orbit, it travels at the same speed as the earth's rotation, thus appearing stationary. GEOs are excellent for TV and radio broadcasting, but produce distracting, half-second delays in interactive voice conversations because. In low earth orbit (LEO), the main dose source is from electrons and protons (inner belt); and in geostationary earth orbit (GEO), the primary source is from electrons (outer belt) and solar protons. The figure above depicts the ionizing radiation environment in space. The graph below shows the annual dose from protons, electrons. The GeoOrbital wheel is by far the easiest way to add electric power to your bike - no tools required! 20 MPH TOP SPEED We use high-powered motors for a top speed of 20 M.P.H. And a pedaling-optional range of up to 25 miles (per-battery).
GEO-XO Overview Fire Weather Health Agriculture Oceans Fact Sheet NOAA’s Geostationary and Extended Orbits (GEO-XO) satellite system is the ground-breaking mission that will advance Earth observations from geostationary orbit. GEO-XO will supply vital information to address major environmental challenges of the future in support of U.S. Weather, ocean and climate operations.
 Also found in: Dictionary, Thesaurus, Medical, Financial, Acronyms, Wikipedia.
Also found in: Dictionary, Thesaurus, Medical, Financial, Acronyms, Wikipedia. geo
[′gyō] (geography)GEO
[¦jē¦ē′ō or ′jē·ō]GEO
(1) Ground based. From the Greek word for 'earth.' See geocaching, geotagging and geodetic coordinates.
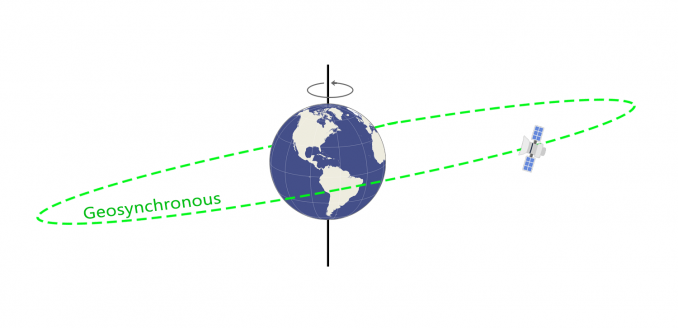
(2) (Geostationary Earth Orbit) A communications satellite in orbit 22,282 miles above the equator. At this orbit, it travels at the same speed as the earth's rotation, thus appearing stationary. GEOs are excellent for TV and radio broadcasting, but produce distracting, half-second delays in interactive voice conversations because of the long round trip from earth and back. LEOs and MEOs, which are closer to the earth, are better for interactive services in real time. See geosynchronous, LEO, MEO and HEO.
| GEOs Appear Stationary |
|---|
| GEOs travel at earth speed and thus appear stationary. Closer to the earth, LEOs and MEOs constantly move across the land. |
Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.
Link to this page:
Advantages of LEO Orbit | disadvantages of LEO Orbit
This page covers advantages and disadvantages of LEO Orbit. It mentions LEO Orbit advantages and LEO Orbit disadvantages.LEO stands for Low Earth Orbit.
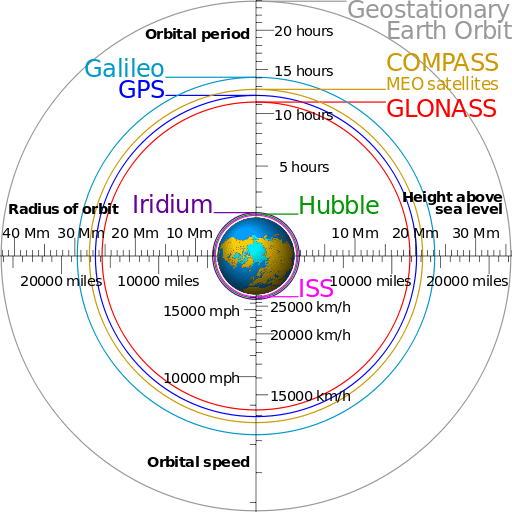
There are three main types of orbits viz. LEO, MEO and GEO based on distances from lowest to the highestfrom the Earth.There are orbits around the earth where satellites are installedafter their launch.Following are the features of LEO orbit.
• Orbit period: 10 to 40 minutes
• Orbit height from Earth: 500 to 1500 Km
• Life of satellite in the orbit: Short
• Propagation loss in the orbit: Least
• Number of satellites to cover entireregions on Earth: 40 to 80
The figure-1 depicts LEO (Low Earth Orbit).
LEO vs MEO vs GEO andsatellite basics for more information.
Advantages of LEO orbit
Following are the advantages of LEO orbit:
➨As it is near to the earth, LEO satelliteslaunced in LEO orbit provides better signal strength. Henceless power (about 1 watt) is needed for transmission.
➨It has least propagation delay (about 10ms) compare toother orbits due to closeness to the Earth.Due to lower latency, it can be used for realtime time criticalapplications.
➨It eliminates need for bulky receiver equipments due tohigher C/N signal ratio.
➨Low price satellite equipments are sufficient forground stations.
➨Better frequency reuse can be achieved due to smaller footprints.
➨It provides high elevation for polar regions of the Earth.Hence better global coverage can be achieved.
Disadvantages of LEO orbit
Low Earth Orbit Satellites
Following are the disadvantages of LEO orbit:
➨As it is at lesser distance above the Earth,it covers less region of the earth. Hencelarge number of satellites are needed to cover the entireregion of the Earth. Hence the installation of such LEObased system is costly.
➨As LEO satellites move constantly and hence service is beinghanded off by each satellite to the next one inthe constellation. Hence succession of satellites are required tocover any region on the Earth.
➨Atmospheric effects are more and hence willcause gradual orbital dis-orientation of the satellites.This requires regular maintenance of satellites to keepthem on track in the LEO orbit.
➨It is only visible for 15 to 20 minutes fromparticular area of the Earth. Hence there is lesstime available for testing and troubleshooting activities.
➨Efficiency to serve populated region is less compare to GEO satellites.
➨Ground station is very complex as it requires to handle frequent handoffsbetween LEO satellites.
➨The complete deployment of LEO constellation is essential tostart the service to the customers. Hence it requires more time to providethe satellite service & mass adoption by the users compare to GEO.
➨LEO satellites have shorter life span (about 5 to 8 years)compare to GEO satellites (about 10 years).
Also refer advantages and disadvantages of MEO >> and GEO >>.
Satellite Communication RELATED LINKS
Advantages and Disadvantages of other wireless technologies
Geo Orbital Wheel For Bikes
What is Difference between
Geo Orbital Electric Bike Wheel
difference between OFDM and OFDMA
Difference between SC-FDMA and OFDM
Difference between SISO and MIMO
Difference between TDD and FDD
FDMA vs TDMA vs CDMA
FDM vs TDM
CDMA vs GSM
RF and Wireless Terminologies
Share this page
Translate this page

